|
|
|
Deptt. Of Computer Systems and Software Engg.
MID TERM TEST 02
CCNW
2K CS Batch
Date: March 20, 2003 Marks: 05 Class ID:
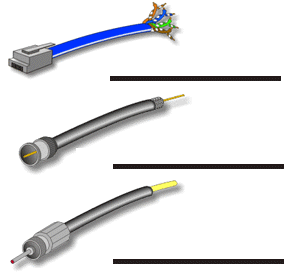
9. Identify Cables
c. Less errors in data transfer d. Higher data transfer speeds
14. Which of layers provides the electrical and mechanical connections between systems?
a. Application b. Presentation c. Session d. Transport
e. Network f. Data Link g. Physical
15. As information structures descend the OSI model layers, they become nested in the information structures below. What is this called?
a. Segmentation b. Fragmentation c. Encapsulation d. Multiplexing
16. What are some of the functions of the upper OSI Layers? (choose all that apply)
a. File Sharing b. file transfer c. network printing d. email
e. data transmission
17. What is the Session Layer's primary responsibility?
a. To ensure end-to-end integrity of data
b. To get user data into session frames
c. To initialize, maintain and tear down a communications experience between two machines
d. To transport frames to the next hop
18. The Transport Layer is responsible for the transition between the upper layers that are concerned with data representation and the lower layers that are concerned with data transfer.
a. True b. False
19. Multiplexing at the Transport Layer breaks up data into smaller pieces called what?
a. MTU b. Packets c. Segments d. None of these
20. When data is being transfered what are the causes of congestion? (check all that applyl)
a. Multiple devices sending data at the same time
b. Destination has too little system memory
c. The source is sending data too fast
d. Data segments fail to arrive at the destination
e. None of the above
21. Which of the following is an example of a connection-oriented protocol?
a. IP b. TCP c. TCP/IP d. None
22. Which of the following are characteristics of connectionless-oriented protocols? (check all that apply)
a. Self-contained, autonomous data entities b. Reliable, error-free delivery
c. Best effort delivery d. Each data unit is part of a data stream
e. May result in lost, dropped and out of sequence packets
23. To accomplish accurate delivery, the Data Link Layer provides the following services: (check all that apply)
a. Machine address determination of both sending and receiving machines
b. Convert "packets" into bits to be delivered over network media
c. Formatting of Network Layer "packets" into frames with machine addresses attached
d. Sequencing and resequencing of frames transmitted out of sequence
24. Which of the following are typical operating speeds for Ethernet 802.3 LANs
a. 3 Mbps b. 5 Mbps c. 10 Mbps d. 100 Mbps
25. Ethernet uses a unique process known as ____ to ensure efficiency and protection from collisions.
a. beaconing b. CSMA/CD c. Broadcasting
26. Transmission process that requires each station to examine every frame to determine whether that frame was meant for it.
a. Framing b. CA c. Media Transmission d. Broadcasting
27. When comparing 10BaseT to 100BaseT, the only difference between them besides speed is:
a. IEEE 802.3 MAC access b. CSMA/CA c. Frame format
d. Network diameter
28. Bridges are faster than switches because the technology is software based
a. True b. False
29. At which layer of the OSI model does bridging occur?
a. Physical b. Data Link c. Network d. Transport
30. Which function of a bridge stops data from crossing over the bridge and into another connected LAN?
a. Flood prevention b. Forwarding c. Bridging d. Filtering
31. A router cannot be configured to utilize bridging technologies.
a. True b. False
32. What are the responsibilities of IP? (check all that apply)
a. Provide connectionless delivery of packets through an internetwork
b. Provide connection-oriented delivery of packets through an internetwork
c. Provide fragmentation and reassembly of packets to support data links with different maximum transmission unit (MTU) sizes.
d. Report routing and delivery problems e. None of the above
33. IP subnetting allows:
a. a hierarchical addressing scheme that promotes network flexibility
b. a network administrator to get more host addresses from a given IP address
c. the outside world to be aware of an organizations internal structure
d. an organization to become a part of the World Wide Web (WWW)
34. Which of the following protocols reports IP routing and delivery problems?
a. TCP b. ICMP c. RIP d. UDP
35. Which of the following statements is true with respect to IPX addressing?
a. Novell IPX addresses are made up a network number and a subnetwork number
b. The network number is assigned by the InterNIC
c. IPX supports hierarchical addressing
d. The node number is taken from the network interface card.
e. Socket
36. What are the two primary functions that routing protocol algorithms perform? (check all that apply)
a. Path determination b. MAC table updating c. Path switching d. MAC table building
37. What are the two protocols used to update routing tables? (check all that apply)
a. Link-state protocols b. Bandwidth protocols c. Router Path protocols d. Distance vector protocol e. Load protocols
38. The control information that is added to a PDU by a layer on a sending device is read by the _________ layer in the peer remote device.
a. Same b. Next Highest c. next Lowest
39. A straight-through cable is used in the following cases (select all that apply):
a. hub to server b. switch to hub c. switch to router d. hub to hub
40. Examples of TCP/IP applications include (select all that apply):
a. TFTP b. SMTP c. Outlook d. Excel e. SNMP f. Word g. NFS
41. The TCP destination port field is ___________ bits.
a. 8 b. 16 c. 32 d. 128
42. These fields are in TCP segments but not in UDP segments:
a. sequence number, acknowledgement number, window, urgent
b. source port, sequence number, acknowledgement number, window
c. sequence number, acknowledgement number, code bits, checksum
d. sequence number, source port, window, urgent
e. source port, acknowledgement number, window, options
f. protocol, sequence number, acknowledgement number, window
43. Select the true statement regarding port numbers.
a. FTP uses port 21; SMTP uses port 53; SNMP uses port 161
b. FTP uses port 21; Telnet uses port 23; SNMP uses port 69.
c. SNMP uses port 25; DNS uses port 53; TFTP uses port 520.
d. TFTP uses port 21; SMTP uses port 25; SNMP uses port 161
e. Telnet uses port 23; DNS uses port 53; SNMP uses port 161
44. When a station sends a message to open a TCP connection, the "well-known" port numbers are typically used
a. as the source port. b. as the destination port
c. as both the source port and the destination port
45. When a station wants to open a TCP connection, the first segment sent includes (select all that apply)
a. the first part of the data stream. b. the ACK bit set. c. the SYN bit set d. the initial sequence number. e. the acknowledgement sequence number
46. DHCP is a modern implementation of:
a. ARP b. RARP c. DNS d. IP
47. In a class C network, the number of usable host addresses is:
a. 0 b. 62 c. 255 d. 254 e. 255
48. An IP address with all bits in the host portion set to zero specifies
a. the first available host address on that network
b. a broadcast to all devices on that network
c. a broadcast to all devices on all networks.
d. the network itself.
49. Subnet bits are
a. taken from the host field of an address
b. taken from the network field of an address
c. always the same number of bits as the host bits.
d. always the same number of bits as the network bits
50. A device has an address 10.19.7.11 and a mask of 255.255.255.0. The range of valid host addresses on the subnet that this device is on is
a. 10.19.0.1 through 10.19.0.254.
b. 10.19.7.1 through 10.19.7.255.
c. 10.19.0.1 through 10.19.255.254
d. 10.0.0.1 through 10.0.0.254
e. 10.0.0.1 through 10.255.255.254
f. 10.19.7.1 through 10.19.7.254